1.1 워크스페이스의 src 폴더로 이동
cd catkin_ws/src/
1.2 패키지 생성
패키지 이름은 hello_world, 의존성은 std_msgs와 rospy
catkin create pkg hello_world --catkin-deps std_msgs rospy
# catkin create pkg <name_of_pkg> --catkin-deps <name_of_dependeces>
1.2.1 파일 구조 확인 (tree apt 이용)
sudo apt install tree
# 설치가 안되어 있다면
tree
1.3 현재 폴더에서 sublime text 실행
subl <address>
subl .
# 점 하나(.)는 현재 위치 기준으로 현재 폴더, 점 두개(..)는 상위 폴더를 의미함
1.4 Package.xml을 보면 지정된 dependancy를 확인할 수 있다.
# Package manifest : 매니페스트는 패키지에 대한 설명과 패키지 라이센서 디펜던시 등의 정보가 제공된다.
# package.xml 이라는 파일에서 관리할 수 있다.
1.5 CMakeLists.txt에는 빌드 정보가 저장되어있다.
1.6 Python code를 통해 subscriber 설정하기
목표 : turtlesim의 정보를 얻어오자 subscriber
Python 코드를 보관할 scripts 폴더 생성
print_turtle_pos.py를 생성
#!/usr/bin/env python
#Python으로 만들어진 ROS내의 모든 코드는 위 줄로 시작해야함 (주석이 아님)
#Python 환경을 지정하는 명령
import rospy #모듈이나 패키지 사용시 불러오는 과정
from turtlesim.msg import Pose # 터틀심 메시지에서 포즈를 가져온다.
def print_turtle_pos(): #노드의 선언과 초기화
rospy.init_node('print_turtle_pos',anonymous=False)
#노드의 이름지정, 초기화 / anonymous 는 다른 노드와의 충돌을 막아준다.
#anonymous 플래그는 같은 이름의 노드가 혼선을 부를 수 있어서
#True로 해두면 노드이름뒤에 유니크한 ID를 붙여준다
rospy.Subscriber("/turtle1/pose",Pose, callback)
#subscriber 노드 선언
rospy.spin()
#subscriber는 토픽이 발행될때마다 받아야하니 항상 대기해야한다
def callback(data):
rospy.loginfo("Turtle Pose X : %s, Y: %s ",data.x, data.y)
# loginfo는 메세지를 출력하는 기능, 디버그때 rosout에 출력하는 기능을 가짐
if __name__ == '__main__':
print_turtle_pos()
# 언더바 두개 네임 : 실행 파일 명
# 이파일이 직접 실행되느냐 라는 질문1.7 실행 권한을 추가하기
chmod +x print_turtle_pos.py
1.8 패키지 빌드
워크스페이스로 이동하여
catkin build hello_world
# catkin이라는 어플리케이션을 이용하여 catkin_ws/src 에 hello_world라는 패키지를 실행 할 수 있게 만들어 준다.
*catkin_tools : 패키지들을 사용할 수 있도록 하는 '빌드' 라는 기능을 제공.
*빌드를 하면 catkin_ws/src 에 있는 소스코드에 대한 정보를 catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash 에 넣어준다.
1.8.1 bashrc 등록
source ~/.bashrc
1.9 subscriber 노드 실행
rosrun hello_world print_turtle_pos.py
2. move_turtle 노드 만들기
2.1 터틀심을 움직이는 토픽이 무엇인지 확인
rostopic list -v
2.2 토픽의 데이터 타입 확인
rostopic type /turtle1/cmd_vel | rosmsg show
2.3 script에 move_turtle.py 새로 만들기 및 코드 작성
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
# turtle1/cmd_ver이 사용하는 데이터형인 geometry_msgs/Twist를 import
def move_turtle():
rospy.init_node('move_turtle', anonymous=False)
vel_pub = rospy.Publisher('/turtle1/cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size=10)
# turtle1/cmd_ver 토픽에 Twist 데이터형으로 선언함
# queue_size는 publish한 데이터를 받지 못할때,
# 계속 데이터를 쌓아둘 수 없어서 그 양을 제한하는 옵션
vel_ref = Twist()
rate = rospy.Rate(10) # 10hz
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
vel_ref.linear.x = 2
vel_ref.angular.z = 2
rospy.loginfo(vel_ref)
vel_pub.publish(vel_ref)
rate.sleep()
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
move_turtle()
except rospy.ROSInterruptException:
pass
# rospy.ROSInterruptException 예외가 발생하는 이유는
# sleep () 후에 실수로 코드를 계속 실행하지 않기 때문
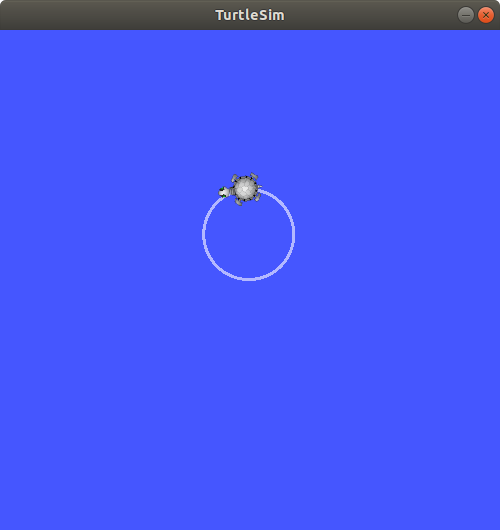
수업이 끝나고 도전해 보길 바란다. <안병구 연구원님>
'Autonomous Vehicle > ROS programming' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 특강 5,6,7일차 : JETBOT 딥러닝 자율주행 따라하기 (5) | 2020.08.08 |
|---|---|
| 특강 3일차 : OpenCV ROS 환경에서 구동 (0) | 2020.07.29 |
| 특강 2일차 : Roslaunch에 대한 이해 (0) | 2020.07.24 |
| 특강 1일차 : ROS 에 대한 이해 (0) | 2020.07.23 |
| Legion Y530 15inch : ROS를 위한 UBUNTU 18.04 작업환경 구축 (0) | 2020.07.20 |



